Fulfil Your Precious Dream of Motherhood with IVF

Embarking on the journey toward motherhood can sometimes be challenging, especially when conception doesn’t happen naturally. In-vitro fertilization (IVF) has emerged as a beacon of hope for many couples and individuals longing to start or expand their families. With advanced medical technology and personalized care, IVF offers significantly increased chances of successful pregnancy. What is IVF? IVF is a fertility treatment where eggs are extracted from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the uterus to establish pregnancy. This method bypasses many barriers to natural conception, such as tubal blockage or male infertility factors. IVF Success Rates in 2025 Factors like embryo quality, sperm health, uterine condition, clinic expertise, and personalized protocols all contribute to these outcomes. Why Choose IVF? IVF is invaluable for conditions such as: What to Expect The IVF process typically involves ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization in the lab, and embryo transfer over a span of several weeks. Emotional support, optimized health, and adherence to treatment protocols enhance the chances of success. Conclusion With modern advancements, IVF has transformed into one of the most effective options to overcome infertility hurdles and realize the dream of motherhood. For many hopeful parents, IVF isn’t just medical treatment—it’s the pathway to joy and family fulfillment.
What is the Normal Liquefaction Time of Semen?
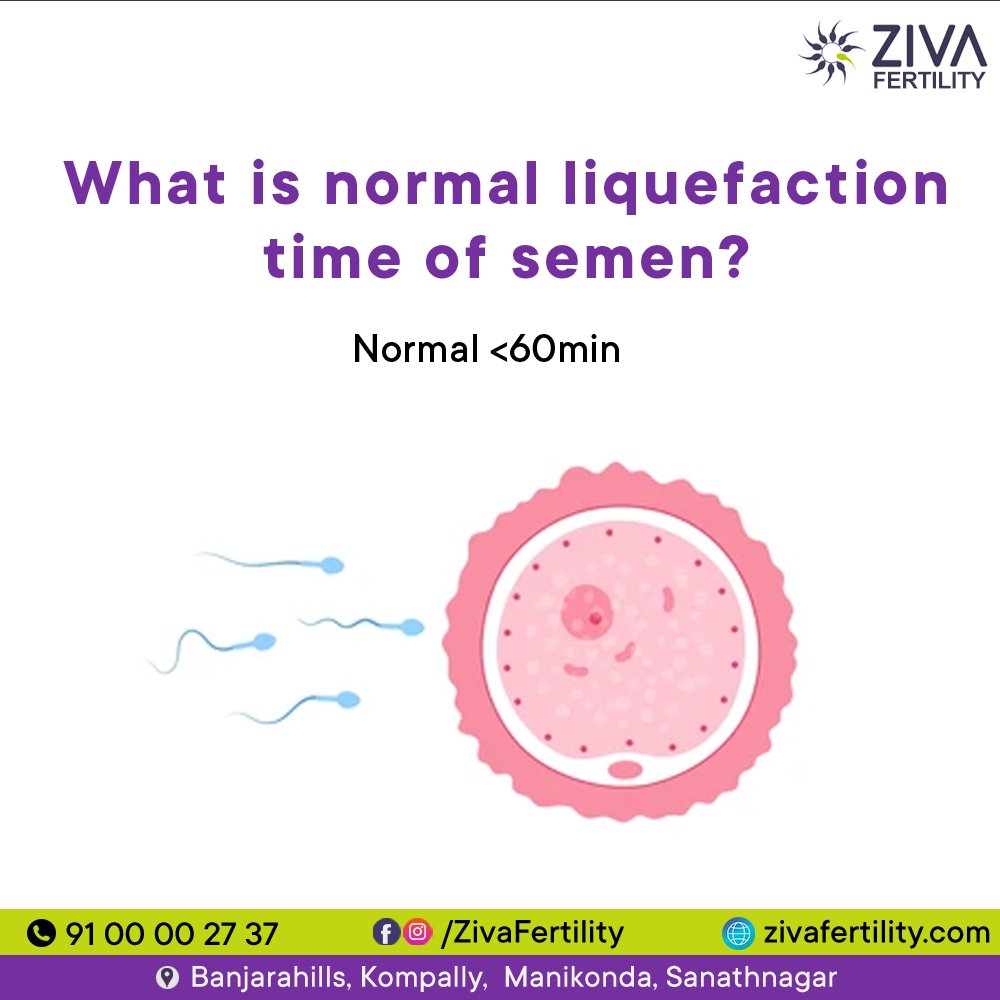
When semen is ejaculated, it initially has a thick, gelatinous consistency designed to help it adhere to the cervical opening. However, for sperm to swim freely and reach the egg effectively, the semen must liquefy, or thin out, within a certain period. This process is called semen liquefaction, which is a crucial parameter measured during semen analysis to assess male fertility. Understanding Semen Liquefaction Liquefaction is caused by proteolytic enzymes present in the seminal plasma, primarily from the prostate gland. These enzymes gradually break down the gel-like coagulum formed immediately after ejaculation to convert the semen into a more liquid, watery consistency. This change increases sperm motility, allowing sperm to swim freely and increase the chances of fertilization. Normal Liquefaction Time Range Factors Affecting Liquefaction Time Several factors can influence the liquefaction time, including: Clinical Significance of Abnormal Liquefaction Delayed or absent liquefaction can negatively impact sperm motility, reducing the chances of natural conception. When semen does not liquefy properly, sperm remain trapped in a thick gel, limiting their mobility and ability to reach the egg. In such cases, additional tests may be required to identify infections or other pathological causes. Treatments targeting the underlying condition often improve liquefaction and fertility outcomes. Conclusion Semen liquefaction is a vital step in assessing male fertility, with the normal liquefaction time being under 60 minutes, typically around 15 to 30 minutes. Abnormal liquefaction may signal accessory gland dysfunction, inflammation, or infection and warrants further clinical investigation. Proper semen liquefaction ensures optimal sperm motility, a key factor in successful conception. If semen analysis reveals delayed or impaired liquefaction, consulting a fertility specialist or urologist can help diagnose and treat potential underlying problems to enhance reproductive health.
What Does a High Volume of Semen Signify?

A high volume of semen, also known medically as hyperspermia, means that a man ejaculates a larger than normal amount of fluid during orgasm. While semen normally contains sperm along with fluids from several glands, an unusually high volume may reflect certain underlying conditions. Possible Significance of High Semen Volume: When to Seek Medical Advice: If combined with symptoms like pelvic pain, painful ejaculation, frequent urination, or difficulties in conception, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended. Semen analysis and other tests can identify if an infection or inflammation requires treatment. Conclusion A high semen volume often reflects increased fluid secretion, potentially from inflammation in accessory organs. While it may not cause direct health issues, it can affect fertility by diluting sperm concentration. Proper evaluation by a fertility specialist or urologist helps address underlying causes and optimize reproductive health.
Dose of Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Recurrent Pregnancy Loss

Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) is frequently used in patients with recurrent pregnancy loss, particularly when underlying thrombophilia or unexplained causes are suspected. The most commonly used LMWH is enoxaparin. Standard Dosage Safety and Prophylaxis LMWH has a good safety profile when used under medical supervision, with rare side effects such as bleeding or thrombocytopenia. It does not cross the placenta, making it a safe choice in pregnancy. Conclusion The standard dose for LMWH in the management of recurrent pregnancy loss is 40 mg/day, with some protocols extending up to 80 mg/day based on individual cases. Treatment duration and monitoring should be guided by a fertility or maternal-fetal medicine specialist to ensure optimal safety and success.
Most Common Uterine Abnormality Associated with Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (RPL): Septate Uterus

Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is a distressing condition where a woman experiences multiple miscarriages, often without a clear cause. One of the significant contributing factors is a structural abnormality of the uterus, with the septate uterus being the most common uterine anomaly linked to RPL. What is a Septate Uterus? A septate uterus is a congenital condition where a fibrous or muscular wall (septum) divides the uterine cavity partially or completely into two sections. This malformation disrupts the normal shape and size of the uterus. How Does It Affect Pregnancy? The septum is often poorly vascularized and may impede proper implantation and growth of the embryo, leading to increased risks of: Prevalence and Impact Studies suggest septate uterus occurs more commonly in women with recurrent miscarriages—up to 18% after two or more pregnancy losses—compared to 2–3% in the general population. Surgical correction by hysteroscopic metroplasty has shown to improve reproductive outcomes, significantly increasing live birth rates and decreasing miscarriage rates in many women. Treatment and Management Hysteroscopic surgery to remove or resect the septum (septoplasty) is the standard treatment option. This minimally invasive procedure helps restore the uterine cavity’s normal shape, improving the chances of successful implantation and maintaining pregnancy. Conclusion A septate uterus is the most common uterine abnormality linked to recurrent pregnancy loss. Proper diagnosis using imaging techniques such as ultrasound or hysteroscopy, followed by surgical management, can substantially enhance fertility outcomes for affected women. If recurrent miscarriages are experienced, consulting a fertility specialist to evaluate for structural anomalies like the septate uterus is essential for effective treatment and hopeful pregnancy outcomes.
Spotting After Embryo Transfer: What You Should Know

Spotting after embryo transfer can be a common and often reassuring sign during the two-week wait before pregnancy is confirmed. Understanding when it happens and what it means can help ease your anxiety during this delicate time. When Does Spotting Typically Occur? Spotting usually occurs around 7 to 8 days after embryo transfer, coinciding with the time the embryo begins to implant into the uterine lining. How Long Does Spotting Last? It is generally self-limiting and lasts for about 3 to 5 days. The bleeding is usually light—spotting or streaks of pink or brown, not like a heavy period. Is Spotting a Positive Sign? Yes, spotting can be an early sign of pregnancy known as implantation bleeding. It indicates the embryo is attaching and creating a connection with the uterus, which sometimes causes tiny blood vessels to bleed slightly. When to Consult Your Fertility Experts While spotting is often normal, it’s important to consult your fertility specialists if: Conclusion Light spotting after embryo transfer is common and usually not a cause for alarm. It may be a hopeful indication of successful implantation, but every woman’s experience is unique. Staying in close contact with your fertility team ensures you receive timely support and guidance throughout your IVF journey.
Male Infertility Issues That Can Be Treated with Surgery

Male infertility can often be addressed through various surgical interventions tailored to specific causes. Surgery not only aims to improve sperm production and quality but also to restore the pathways necessary for sperm to travel. Here are some common male infertility issues that can be effectively treated with surgery: 1. Varicocele Repair (Varicocelectomy) A varicocele is an enlargement of veins within the scrotum that can impair sperm production by increasing testicular temperature and reducing oxygen supply. Microsurgical varicocelectomy involves tying off these enlarged veins to improve blood flow, which often improves sperm count and quality and increases the chances of conception. 2. Vasectomy Reversal Men who have previously undergone vasectomy for contraception can opt for surgical reversal. Vasovasostomy reconnects the severed vas deferens tubes, restoring sperm flow. In cases where the vas deferens cannot be reconnected, vasoepididymostomy connects the vas deferens to the epididymis, bypassing blockages. 3. Sperm Retrieval Procedures For men with no sperm in the ejaculate due to obstruction or poor sperm production, surgical sperm retrieval techniques like microsurgical testicular sperm extraction (microTESE) or percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) can extract viable sperm directly from testicular or epididymal tissue. Retrieved sperm can then be used in assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF-ICSI. 4. Transurethral Resection of the Ejaculatory Duct (TURED) This surgery removes blockages in the ejaculatory ducts that prevent sperm from mixing with semen, restoring the ability to ejaculate sperm. 5. Repair of Obstructive Azoospermia Surgical interventions can correct congenital or acquired obstructions in reproductive ducts that block sperm transport, improving natural fertility or sperm availability for ART. Conclusion Surgical treatments play an essential role in managing male infertility caused by anatomical abnormalities, obstructions, or conditions like varicocele. Advances in microsurgical techniques have improved success rates and recovery times significantly. However, surgery is usually considered after thorough evaluation and is often combined with assisted reproductive technologies to maximize pregnancy chances. Consulting a specialized urologist or fertility expert is the best way to determine if surgical treatment is suitable for your specific infertility cause.
I am an Infertile Woman and I Want to Have a Baby: What You Need to Know

Facing infertility can feel overwhelming, but understanding the journey ahead can empower you to take proactive steps toward achieving your dream of becoming a mother. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate fertility challenges with knowledge, hope, and support. Understand Your Diagnosis Infertility can arise from numerous causes—ovulation disorders, tubal issues, uterine problems, male factor infertility, unexplained reasons, or age-related declines. Thorough evaluation by a fertility specialist, including medical history, physical exams, and tests like hormone levels, ultrasounds, and semen analysis for your partner, are essential to pinpoint the cause. Explore Your Treatment Options Depending on your diagnosis, treatments range from lifestyle changes and medications to advanced assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as: Emotional and Psychological Support Infertility can take an emotional toll due to uncertainty, hormonal changes, and treatment stress. Seek counseling, support groups, or therapy to help manage anxiety, relationships, and coping. Lifestyle Choices Matter Maintain a balanced diet, regular moderate exercise, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, manage stress, and ensure adequate sleep for optimal reproductive health. Be Patient and Stay Positive Fertility treatment is often a marathon, not a sprint. Success rates improve with persistence and working closely with your care team. Celebrate small victories and maintain hope. Seek Expert Care Choose a reputable fertility clinic with experienced specialists and a compassionate approach. Personalized evaluation and tailored treatment plans increase your chances of success. Conclusion While infertility poses challenges, many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies with appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Educate yourself, build a support network, and collaborate with your fertility care team to navigate this journey confidently toward motherhood. Your hope and determination are vital companions on this path.
Treatment Options for Infertility

Infertility affects many couples, but advances in medicine offer a range of treatment options tailored to different causes and individual needs. Understanding the main fertility treatment choices helps couples make informed decisions in their journey toward parenthood. 1. Medications Fertility drugs stimulate ovulation or improve egg quality. Common medications include: 2. Surgery Surgical interventions may correct anatomical problems such as: 3. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) In IUI, prepared sperm is placed directly into the uterus during ovulation, increasing the chances of sperm meeting the egg. IUI is less invasive and commonly used for mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or cervical factor infertility. 4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) IVF involves fertilizing eggs with sperm outside the body in a laboratory, then transferring the embryo(s) into the uterus. IVF is effective for various infertility causes, including tubal blockage, severe male infertility, and unexplained cases after other treatments fail. 5. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) ICSI is a microinjection technique where a single, carefully selected sperm is injected directly into an egg. It is commonly used in cases of severe male infertility or previous IVF failures. 6. Using Donor Eggs, Donor Sperm, or Donor Embryos For couples with poor egg or sperm quality, or genetic concerns, donor gametes or embryos offer an option to achieve pregnancy. This approach requires counseling and legal considerations. Conclusion Infertility treatment is highly personalized based on causes, age, medical history, and patient preferences. From medications and surgery to assisted reproductive technologies like IUI, IVF, and ICSI, numerous options exist to help couples achieve their dream of parenthood. Consulting a fertility specialist early ensures the best chance of successful treatment tailored to individual needs.
How Soon After a Miscarriage Can You Get Pregnant?

Experiencing a miscarriage is often emotionally and physically challenging, and many women wonder when it is safe and appropriate to try conceiving again. The timeline for getting pregnant after a miscarriage varies based on individual health, emotional readiness, and the nature of the pregnancy loss. Physical Readiness You may be able to get pregnant as soon as your menstrual cycle begins again, which is usually about four to six weeks after a miscarriage. Ovulation can occur even before your first post-miscarriage period, sometimes as early as two weeks after the loss. Emotional Considerations Beyond the physical, it’s important to consider your emotional healing. Grieving and processing the loss is vital before embarking on another pregnancy journey. Medical Guidance Traditionally, some doctors recommended waiting three months before trying again, and organizations like the World Health Organization have suggested six months. However, recent studies show that conceiving within a few months of miscarriage does not increase the risk of complications and may actually lower the risk of subsequent miscarriage. When to Consult Your Doctor If you had surgical procedures like dilation and curettage (D&C), complications, recurrent miscarriages, or later pregnancy losses, your doctor may advise waiting longer and perform evaluations or treatments before pregnancy attempts. Conclusion Physically, many women can get pregnant shortly after a miscarriage once their cycles return. Emotional readiness and medical advice should guide timing for trying again. Open communication with your healthcare provider ensures a safe and supported path to a healthy pregnancy when you are ready.
