As per the modern standards of living all around the world, almost 15% of couples are having difficulty conceiving. If the couple hasn’t seen results even after trying for over 12 months, it’s time to visit a Fertility Specialist Clinic like ZIVA. There is so much information about fertility out there that some of these terms are used quite often and can confuse the couple. These terms are related to both male and female infertility. Causes of infertility, symptoms, tests, and treatment modalities are all the various things that the couple should be able to follow. Choosing to visit a Fertility centre is itself a major decision, so we would like to make this as easy as possible for you. After reading this blog, you will be well aware and more prepared on your first or next visit to a fertility clinic.
- Assisted reproductive technique (ART) – Assisted reproductive techniques are a common name for an umbrella of fertility treatment. These fertility treatments are suitable for both male and female infertility. ART is chosen for couples who haven’t had success despite medication or surgical treatment. Single parents or couples who have crossed the reproductive age also opt for them.
- Beta hCG: Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin is the main hormone normally produced by pregnancy. hCG can stimulate ovulation. Beta hCG levels help in monitoring the growth of early pregnancy. For every 48 hours, the Beta hCG levels should be roughly double.
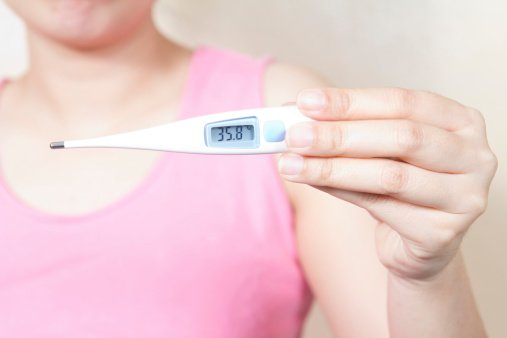
- Basal body temperature (BBT): The body temperature before getting out of bed is called BBT. BBT is the lowest temperature of the body during the day. BBT is crucial to know if you are ovulating. One can measure BBT with a basal thermometer. During the period of ovulation, BBT increases by about half a degree following the release of an egg. Starting the day of the temperature rise, you will be most fertile for the next two to three days.
- Blastocyst: Five to six days after the fertilization of a zygote, it enters the Blastocyst stage. For a few days, the cells in the blastocyst continue to divide and then implant into the uterine wall. After the blastocyst implants in the uterine wall, it develops into an embryo in the next ten to 12 days after fertilization.
- Cryopreservation: More and more women are opting for late pregnancy. However, the older the age, the quality of eggs reduces. Hence modern medical science has provided a method of freezing the egg. As explained above, more than one embryo might get created in the IVF process. The couple might choose to use only one embryo. So in both cases of egg or embryo preservation, the Cryopreservation process is used. Cryopreservation is a process where the egg or embryo(s) are stored below the freezing point. When it is time to use them, they are thawed and used as per the ART method.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: If the pregnancy occurs outside the uterus and generally on the fallopian tube, it is termed an ectopic pregnancy. These pregnancies are removed surgically or by medication. If not treated, there is a high risk of severe pain and bleeding.

- Egg or Embryo Donation: An infertile woman can use a fertile woman’s fresh or frozen donor eggs to do an ART procedure. In rare cases, unused embryos from other reproductive procedures are donated to other women. The recipient can use them in an ART to get pregnant.
- Endometriosis: The tissue lining the inside of the uterus is called an Endometrium. For women suffering from Endometriosis, the endometrium normally inside the uterus develops in other places. It could grow outside the uterus on the fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing bleeding, scarring, pelvic pain, and infertility.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): The most popular and widely used assisted reproductive technique is IVF. IVF is a process In which the egg and sperm are manually combined inside a laboratory. Fertilization is done in the lab to create a healthy embryo. After a few days, the embryo is implanted into the uterus. IVF has another variation where Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and IVF are combined. The procedure is the same as an IVF, but a single sperm is injected directly into an egg in the lab. After fertilization, the embryo is implanted into a woman’s uterus or fallopian tubes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a major condition affecting most women of reproductive age. This is a hormonal imbalance marked by any two of the following three symptoms:
- Overproduction of androgens (male hormones)
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- An ultrasound demonstrating polycystic-appearing ovaries.
There are many causes for PCOS to occur. Out of them predominantly are lifestyle, obesity, stress, etc.
The list of female fertility glossaries is exhausting. Here we have tried to identify a few of the most commonly used terms in female fertility. Still, when you visit the ZIVA fertilityy clinic, we will ensure you completely understand everything. Please visit our website https://zivafertility.com/ or contact us at +91-9100002737, +91-9392834024, and Info@zivafertility.com