Infertility is a more common problem than they realise, but fortunately, having fertility issues doesn’t automatically mean that you won’t be able to have your child. Many treatments and procedures will drastically increase the chances of conception. Infertility implies an issue with your reproductive system that is preventing you from impregnating your female partner. When a couple has repeated unprotected sex for over a year, but there is no pregnancy, then either one of the partners could have infertility issues.
What is the commonality of male infertility?
Infertility is known to affect one in every six couples who are trying to conceive. As per estimates, in about 30% of all cases of infertility, the contributing factor is male factor infertility. For a successful conception, producing healthy sperm by the male and nutritious eggs by the female is crucial. Apart from this, the female should have unblocked fallopian tubes so that the sperm can fertilise the egg. After fertilisation, the embryo must be able to implant in the female’s uterus.
Just conception is not enough; the embryo must be healthy for the pregnancy to continue to full term.
When do males face infertility?
Males do not exhibit outward symptoms of infertility like women. They might ignore their fertility until they are unable to father a child. But below are some of the warning signs
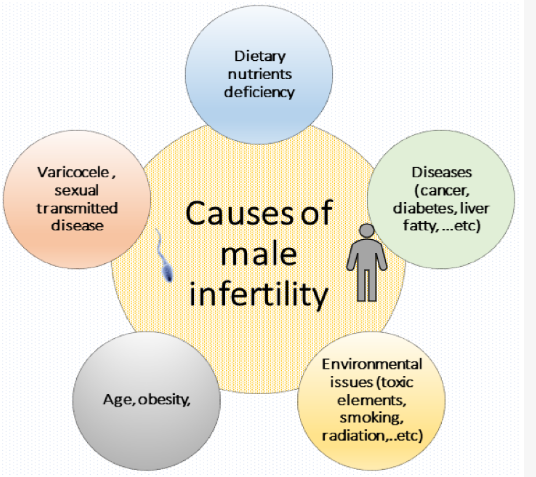
- Being overweight or obese.
- You are 40 or older when you think of fathering a child.
- Excess radiation exposure.
- Have been working in a toxic environment which includes lead, calcium, pesticides or mercury.
- Excess consumption of tobacco, marijuana or alcohol.
- Regularly consume cyproterone, flutamide, spironolactone, bicalutamide, cimetidine or ketoconazole.
- You’re surrounded by a constant heat-raising environment, such as frequently using a sauna, hot tub or wheelchair.
- Born with undescended testicle(s).
- A medical condition called varicoceles means that the veins in the scrotum are swollen or widened.
- Have a history of testosterone injections, implants or topical gel for low testosterone.
- Azoospermia: This is a condition where the male cannot produce sperm cells.
- Oligospermia: The production of sperm happens, but it is low and of poor quality sperm.
- Genetic diseases: Klinefeflter’s syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, microdeletion and more.
- Malformed sperm: Sperm with a short lifespan, which cannot survive till it can fertilise the egg.
- Medical history: Diabetes, autoimmune disorders, cystic fibrosis and some infections.
- Varicoceles: The veins of the testicles are more prominent than average, which produces a heating effect that affects the shape or number of your sperm.
- Cancer treatments: Chemotherapy, radiation or surgery involving removal of the testicles.
- Unhealthy habits: Regular substance use, including alcohol, smoking and drugs.
- Accident or a severe blow to your testes.
- Any disorders that affect your hypothalamus or pituitary glands can affect your infertility.
Non-medical impact of male infertility
Apart from the noticeable effect, which is unable to conceive, it also has adverse psychological and emotional impacts. Most couples make conception the sole focus of their lives, leading to feelings of depression, loss, grief, inadequacy and failure.
If you or your partner are experiencing any of these feelings, please seek professional help experienced in dealing with infertility issues.
Diagnosis of male infertility
Following a physical examination, the fertility specialist will do a semen analysis to determine the following:
- Sperm volume: Amount of sperm per ejaculate.
- pH: A measurement of acidity or basicity.
- Sperm concentration: Number of sperm per millimetre of semen.
- Total sperm count: Number of sperm in your whole ejaculate.
- Velocity: How fast your sperm travels.
- Linearity: How straight your sperm moves.
- Morphology: Size and shape of your sperm.
- Colour.
- Viscosity: How fast your semen liquefies.
- Viability of sperm, or ability to survive.
- Morphology, or quality and shape.
- Motility is your sperm’s ability to move to the egg and fertilise it.
How is male infertility treated?
With modern technology and methods, the number of treatment options for male infertility has expanded. Depending on the cause of infertility, treatments may include:
Medications: Hormone therapy which can increase the number of sperm.
Lifestyle changes:–
- Healthy body weight
- Stop smoking, drinking, using marijuana, recreational drug use.
Surgeries:
Vasectomy reversal: This is a standard procedure where your vas deferens, which is the tube in the scrotum through which your sperm passes, is carefully sewn back together.
Sperm Retrieval: To use the sperm in ART procedures, the sperm is retrieved via a biopsy.
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection: A single sperm can be physically injected into an egg, giving 90% of all infertile males the potential to conceive their genetic child.
In vitro fertilisation: Fertilisation is accomplished by combining the eggs with the sperm in a culture dish or injecting a single sperm into each mature egg. After fertilisation, healthy embryos are placed into the uterus through a small catheter inserted through the cervix.
We at ZIVA Fertility have decades of experience treating infertility in men. We offer both medical and counselling services. Please be open with us; we will help you realise your dreams of becoming a father. For more information, please get in touch with us at +91-9100002737, +91-9392834024, and info@zivafertility.com or visit our website https://zivafertility.com/.