Many couples worldwide are opting for ART – Assisted Reproductive Techniques. Amongst all the ART’s, IVF – In Vitro Fertilization process is the most popular one. In IVF, the embryo is fertilized outside the woman’s body. In this blog, we will understand everything about how this externally fertilized embryo is transferred into a woman’s uterus.
What is an embryo transfer?
In an IVF, medicines are given so that women release more eggs. Mature eggs are collected (retrieved) from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab resulting in an embryo. The last part of an IVF is transferring these embryos into the woman’s uterus. Once the embryo attaches itself to the uterus, conception is successful. IVF and embryo transfer are needed when natural fertilization is not an option or has difficulty occurring. Below are the circumstances under which an embryo is transferred:-
- If a woman has an ovulation disorder, fewer eggs are available for successful fertilization.
- For successful fertilization, at least one fallopian tube must work properly. If the tubes are damaged, the embryos cannot reach the uterus.
- If a woman has endometriosis, the uterine tissue implants and grows outside the uterus.
- Small benign tumours known as fibroids grow on the walls of the uterus. These fibroids prevent the eggs from planting themselves into the uterus, preventing pregnancy.
- In men, low sperm production, poor movement of the sperm, damaged testes, or semen abnormalities are some reasons for infertility.
Couples diagnosed with any of the above conditions opt for an IVF and embryo transfer an option.

Embryo transfer process
Before the embryo transfer
Metabolomic profiling is done around 2 or 3 days before the embryo transfer. It is a process where the most beneficial eggs are selected based on various factors. After fertilizing the best eggs, they are left for culturing for 1-2 days. After a couple of days, embryos are formed. However, if more than required healthy embryos develop, some are frozen for future use.
On the day of the embryo transfer
To keep the vaginal walls open, a speculum is inserted into the woman’s vagina. The doctor is guided by ultrasound for accurate results. A catheter is passed through the cervix directly into the womb, through which the embryos are passed. Thus, the embryos are directly placed inside the womb. The only discomfort might be a full bladder required for an ultrasound. Hence, the procedure is short; the bladder discomfort won’t be for long. Otherwise, it is a pain-free process and sedatives are used rarely.
After the embryo transfer
Everyday experiences after the embryo transfer include cramping, bloating, and vaginal discharge. The doctor will ask you to come after a couple of weeks for follow up. The embryos might have been implanted within that time frame, and you are pregnant.
Types of embryo transfer
Let us understand the various types of embryo transfer:-
Fresh embryo transfer: Freshly cultured embryos are directly transferred to the woman’s uterus.
Frozen embryo transfer: More embryos are formed after culture in a happy scenario. Some of them are used in the first transfer, and the rest are frozen. After a few years, if women want to get pregnant again, frozen and stored are thawed and transferred to the uterus.
Blastocyst embryo transfer: Sometimes, the embryo may develop into blastocysts. On the third day, the blastocyst is transferred, which has a higher pregnancy success rate than embryo transfer. But studies show that this poses risks in the later stages of pregnancy, hence not always recommended.
Assisted hatching (AH): In assisted hatching, the embryo’s outer layer is weakened before transferring to the uterus. This is used for women who are using frozen embryos.
For how long can embryos be frozen?
Embryos can be technically frozen/cryopreserved for years. Their quality does not deteriorate over time.
How many embryos are transferred in one session?
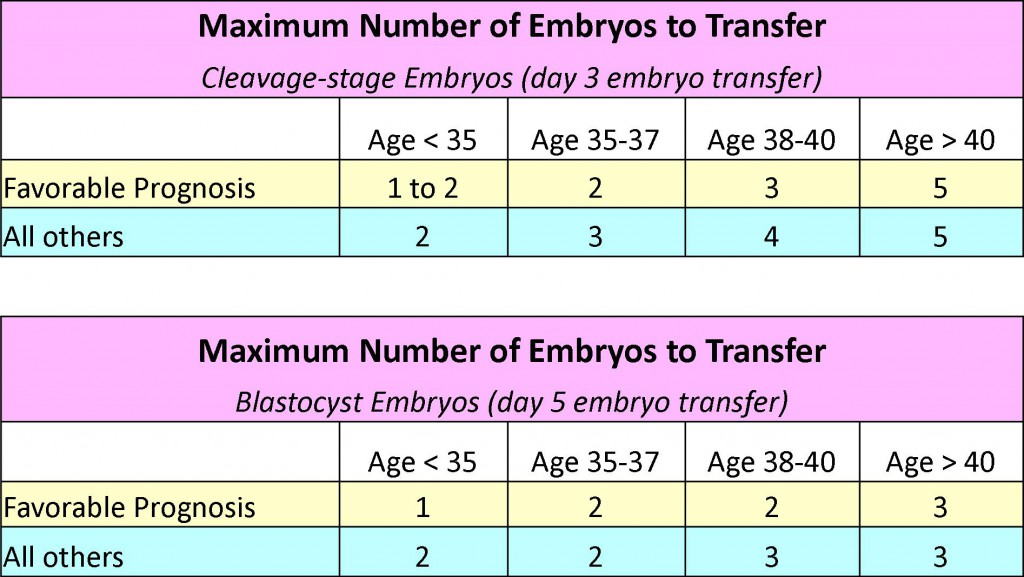
The number of embryos transferred is decided based on the age and the reason for infertility. For women under 35, only one healthy embryo is transferred. But for any aged woman at the max, two embryos are transferred. But if the woman’s chances for pregnancy are low due to any of the aforementioned reasons, a technique called heavy load transfer (HLT) is used. HLT boosts pregnancy rates to an acceptable level. In HLT, three or more embryos are transferred to the uterus.
Success rates of embryo transfers
Fresh embryo transfer has a 23 per cent successful pregnancy rate, whereas frozen embryos had an 18 per cent pregnancy rate. Individual success rates depend on:-
- Age
- Cause of infertility
- Ethnic backgrounds
- Genetic disorders
Risks of embryo transfers
Pregnancy after an embryo transfer has the same risks as natural conception. If there is any additional risk, then it is multiple pregnancies. These multiple pregnancies increase the risk of stillbirth and children born with disabilities.
How soon to do a pregnancy test after IVF?
About 10-12 days after the transfer, a blood test will be advised to find out if she is pregnant. If embryo implantation has occurred, HCG hormone will be detectable in the mother’s blood at that time.
ZIVA fertility center has experts in Embryo Transfers. We will give you all the facts beforehand and be with you throughout the process. Our friendly team is there to answer any questions you might have. Reach us at +91-9100002737, +91 93474 06900 or email us at Info@zivafertility.com