Secondary infertility refers to the inability to conceive after having successfully achieved pregnancy in the past, whether through natural means or assisted reproductive technologies. It can affect couples who have one or more children but are experiencing difficulties in trying to conceive again. Various factors can contribute to secondary infertility, including age, health issues, lifestyle factors, or changes in either partner’s reproductive health. It’s important for couples experiencing this to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and potential treatment options.
How do you know if you have secondary infertility?

You might suspect secondary infertility if you’ve been trying to conceive for a year or more (or six months if you’re over 35) without success, despite having been able to get pregnant before. Other indicators can include:
- Changes in Menstrual Cycle: Irregularities in your cycle or changes in menstrual flow can be a sign of underlying issues.
- Age: As both partners age, fertility can decline, which may lead to difficulties in conceiving.
- Health Changes: Medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or issues with sperm quality can affect your ability to conceive.
- Lifestyle Factors: Changes in weight, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or high-stress levels can impact fertility.
- History of Miscarriages: If you have experienced miscarriages, it could indicate underlying problems that may affect future pregnancies.
If you suspect secondary infertility, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored guidance.
What are the causes for secondary infertility?

There are several potential reasons for secondary infertility, including:
- Age: As women age, their fertility declines, and men may also experience reduced sperm quality and quantity.
- Ovulation Disorders: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hormonal imbalances can lead to irregular ovulation or anovulation.
- Uterine or Fallopian Tube Issues: Conditions such as fibroids, polyps, or scarring from previous surgeries can interfere with implantation or sperm transport.
- Endometriosis: This condition can affect the reproductive organs and disrupt normal fertility.
- Sperm Issues: Male partners may experience decreased sperm production, motility issues, or other problems related to sperm quality.
- Unexplained Infertility: In some cases, no clear cause can be identified despite thorough testing.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and high-stress levels can negatively impact fertility.
- Previous Birth Complications: Issues during a previous pregnancy or childbirth can affect future fertility.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or autoimmune diseases can also play a role.
It’s important for couples facing secondary infertility to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis tailored to their specific situation.
What are the treatments for secondary infertility?
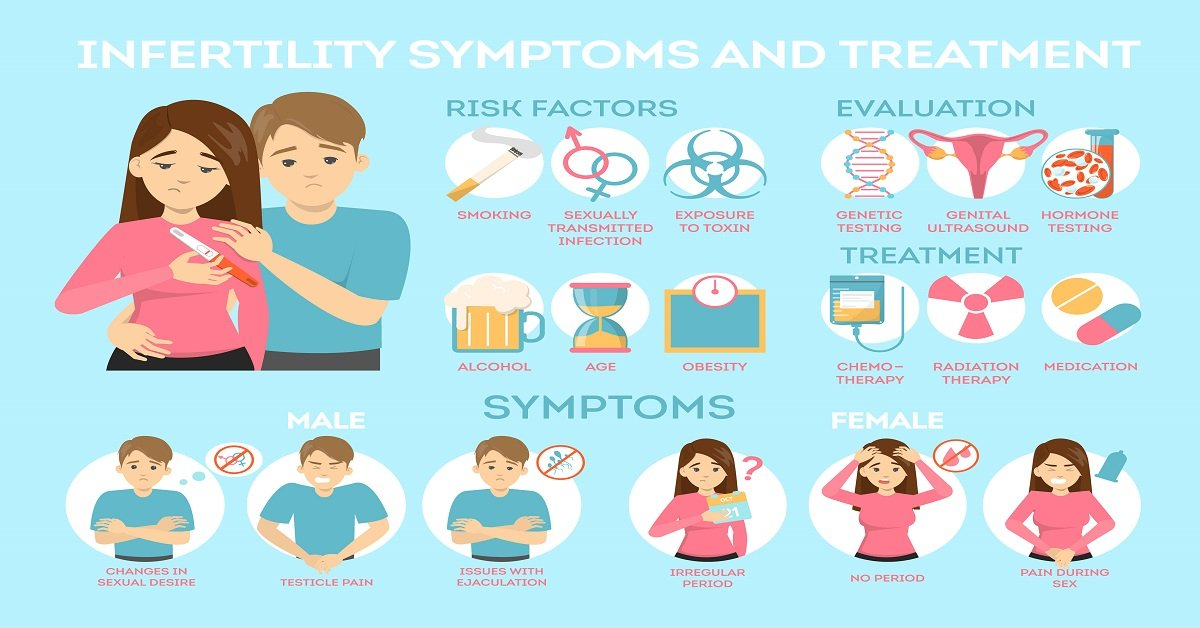
Treatment for secondary infertility depends on the underlying cause and may include the following options:
- Lifestyle Changes: Modifying lifestyle factors such as achieving a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, managing stress, and improving diet can enhance fertility.
- Medication: Hormonal treatments can help regulate ovulation for women who have ovulation disorders. Clomiphene citrate or letrozole are commonly prescribed to stimulate ovulation.
- Surgery: If there are anatomical issues such as fibroids, polyps, or endometriosis, surgical interventions may be necessary to remove obstructions or repair damaged reproductive organs.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): This procedure involves placing sperm directly into the uterus during ovulation to increase the chances of fertilization.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries, fertilized in a lab with sperm, and the resulting embryos are transferred back into the uterus.
- Addressing Male Factors: Treatments for male infertility may include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures to retrieve sperm directly if needed.
- Counseling: Emotional support and counseling can be beneficial, especially if the stress of infertility is affecting the relationship.
- Fertility Preservation: For those who may want to delay conception due to health issues, egg or sperm freezing can be an option.
It’s essential for couples experiencing secondary infertility to consult with a fertility specialist to identify the most suitable treatment based on their unique circumstances.Always consult us at ZIVA Fertility clinics before making significant lifestyle changes, especially when trying to conceive.For more information, please visit our website https://zivafertility.com/ or contact us at +91-9100002737 or +91-9347406900.