Of Late, more and more women are opting for fertility treatments for various reasons, each deeply personal and often complex. As women age, their fertility naturally decreases. Women over the age of 35 might choose fertility treatments to increase their chances of conceiving. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) can affect a woman’s fertility. Treatments can help overcome these barriers to pregnancy. Some couples experience unexplained infertility, where no clear cause is found despite extensive testing. Fertility treatments can offer hope to these couples.
If a partner has issues with sperm count, mobility, or morphology, a couple might turn to fertility treatments that can assist with these problems. Women who are about to undergo treatments that might affect their fertility, such as chemotherapy, may opt for fertility-preserving procedures like egg freezing. Couples with a high risk of passing on genetic disorders to their offspring might choose IVF combined with preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) to ensure a healthy baby.

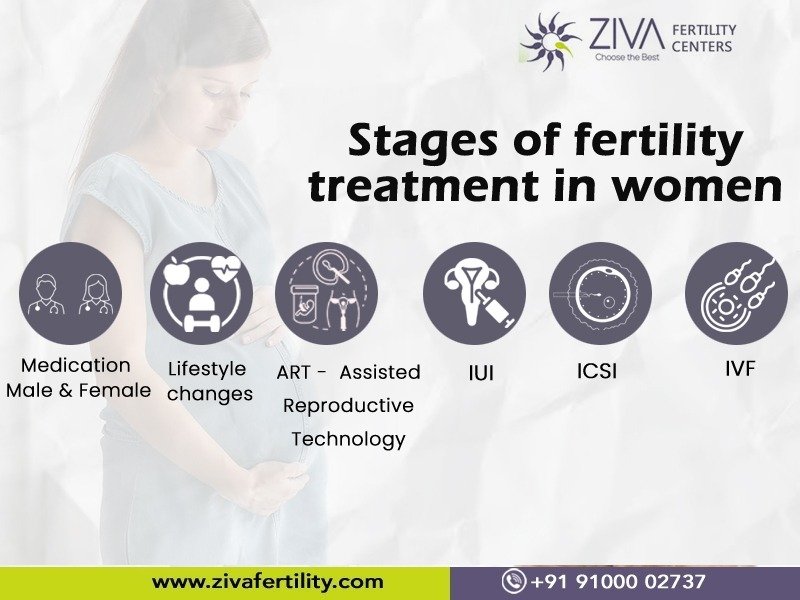
Stages of fertility treatment in women
Fertility treatments for women can be categorized into several key stages, designed to enhance the likelihood of conception. These stages are tailored to individual needs, based on factors like age, the reason for infertility, and personal preferences. Here’s an outline of common stages in fertility treatment:
Stage 1. Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
This is the first step, where health care providers conduct various tests and assessments to understand the underlying causes of infertility. It might include physical exams, blood tests to check hormone levels, ovulation tracking, and imaging tests like ultrasound.
Stage 2. Lifestyle Changes and Medication
Adopting a healthy lifestyle not only improves overall well-being but also optimizes the effectiveness of fertility treatments. Here are some crucial lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being either underweight or overweight can affect fertility. Aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise to achieve a healthy BMI.
- Nutrition: A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support reproductive health. Certain nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, and Omega-3 fatty acids are particularly important.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: High consumption of caffeine and alcohol can negatively impact fertility. It’s advisable to limit intake while trying to conceive and during treatment.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking has been linked to reduced fertility and can also harm a developing fetus. Quitting is one of the best steps you can take for your fertility and overall health.
- Manage Stress: High-stress levels can interfere with hormones needed for ovulation, implantation, and early embryo development. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and counseling can be beneficial.
- Avoid Certain Environmental Toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants can affect fertility. These include pesticides, lead, and phthalates found in some plastics. Try to reduce exposure as much as possible.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Continuous medical support and guidance can help address any underlying health issues that may affect fertility and ensure that any fertility treatments are working as intended.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get sufficient, quality sleep is crucial. Sleep affects the production of several hormones that play key roles in fertility.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for all bodily functions, including fertility. Drinking adequate water each day helps maintain a healthy environment for cellular processes involved in conception.
- Limit Exposure to Electronic Devices: Although more research is needed, some studies suggest that excessive exposure to light from screens may affect melatonin production and menstrual cycles.
Stage 3. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART):

Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) encompasses a variety of procedures aimed at helping individuals and couples achieve pregnancy. This set of technologies is primarily utilized when other methods of achieving pregnancy, such as timed intercourse or fertility drugs, have not been successful. For women facing fertility challenges, ART can offer hope and a path to parenthood. The most common and effective forms of ART include:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): This is the most well-known form of ART. It involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a lab. Once the embryos develop, one or more are transferred to the woman’s uterus. IVF is often used in cases of blocked fallopian tubes, severe male infertility, and unexplained infertility, among others.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): This procedure is similar to IVF but with a key difference. A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to achieve fertilization. ICSI is particularly useful when there are issues with the sperm, such as low motility or count.
- Egg Freezing (Oocyte Cryopreservation): This technology allows women to preserve their fertility by freezing their eggs at a young age to use later. It’s an option for women who aren’t ready to have children but want to keep the possibility open or for those facing medical treatments that might affect fertility.
- Embryo Freezing: Similar to egg freezing, this method involves freezing embryos for future use. This is often used when there are surplus embryos from an IVF cycle that the couple wishes to use later.
- Donor Eggs and Sperm: Some couples may need to rely on donated eggs, sperm, or embryos to achieve pregnancy. This can be due to a variety of reasons including age-related infertility, genetic diseases, or severe sperm/egg issues.
- Gestational Carriers (Surrogacy): When a woman can produce healthy eggs but cannot carry a pregnancy to term, gestational surrogacy can be an option. In this process, another woman carries the pregnancy. The embryo implanted in the gestational carrier’s uterus can be from the intended mother’s egg and the partner’s sperm, a donor egg fertilized with the partner’s sperm, or a donor embryo.
Each of these technologies has its protocols, costs, and potential for success, and they often bring up complex emotional, ethical, and legal issues. Individuals and couples need to consult with fertility specialists to understand the options, success rates, and whether any of these technologies are appropriate for their specific situation.
Stage 4. Third-party Assistance
Some couples might need to consider donor eggs, donor sperm, or a gestational carrier (surrogate) as part of their fertility treatment.
Stage 5. Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Acupuncture, yoga, and other holistic therapies may be suggested to support overall well-being and reduce stress throughout the fertility treatment process.
Stage 6. Counseling and Support
Emotional and psychological support is crucial during fertility treatments. Many find counseling, support groups, and therapy beneficial to cope with the emotional stress and challenges of infertility.
Each step needs to be thoroughly discussed with a healthcare provider to tailor the treatment plan according to the specific needs and preferences of the individual or couple. Choosing to pursue fertility treatments involves many considerations, including emotional, physical, and financial factors. Each person or couple’s journey to parenthood is unique, and fertility treatments can be an invaluable aid in realizing their dreams of having a child. For more information please visit our website https://zivafertility.com/ or contact us at 91-9100002737, +91-9347406900, info@zivafertility.com