A successful pregnancy is a joyous occasion not only for the couple but also for their families. In the current internet generation, the couple would want to know about every stage of their baby’s growth. It is also good to be educated about what stages your baby undergoes while growing inside your womb. In this blog, we will give you a comprehensive list of the main stages that the embryo undergoes as it is developing into a healthy baby.
Stage 1 – Fertilization
Fertilization, in the simplest terms, means combining the female gamete (egg) and the male gamete (spermatozoa). This union can occur naturally or via an Assisted Reproductive Technique (ART), but in either case, the union results in a “zygote”. During ovulation, a woman releases a single egg into the Fallopian tubes. To facilitate fertilization, the woman’s cervical mucus becomes thin so that the sperm can survive and pass through more effectively. Certain special secretions assist the sperm in swimming through the cervix and reaching the uterine tube. Fertilization can take place anywhere within 24-72h. After successful fertilization, the zygote moves towards the uterus, and it divides into the next stage, thus forming a blastocyst.
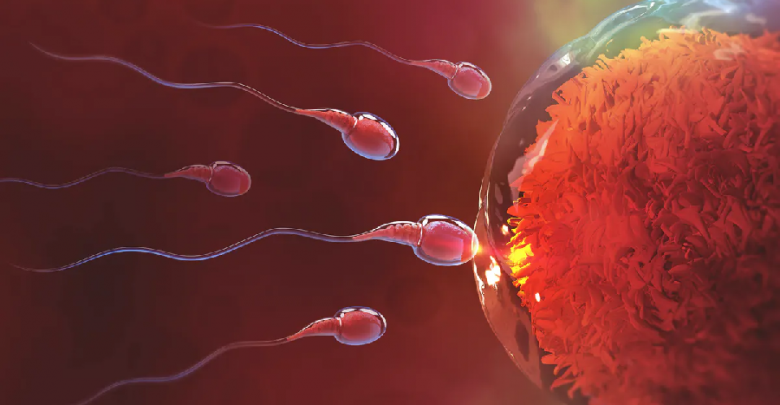
Issues that could obstruct Fertilization
No Sperm/Egg:
- If the woman is suffering from anovulation where no egg is released
- If the sperm is unable to reach the egg due to azoospermia
- Inability Low sperm count.
The inability of the sperm to reach the Egg:
- Poor sperm motility
- Poor chemotaxis is the sperm’s ability to navigate toward the egg
- If the woman’s cervix is not thin enough for the sperm to reach the egg.
Sperm Penetration:
- Poor morphology
- The abnormal shape of the sperm makes it harder to penetrate an egg.
- Sperm uses a chemical reaction, called an acrosome reaction, to pierce a hole in the egg so that it can go through. A poor acrosome reaction could also inhibit fertilization.
Stage 2- Blastocyst Development and Implantation
The embryo is created from a small group of cells that constantly divide inside a complicated structure called “blastocyst”. It comprises inner cells, outer cells, and fluids. Just like an eggshell, zona pellucida is a protective cover around the blastocyst while it is maturing. The outer cells situated below this cover create the placenta in the next stage. The inner cells of the blastocyst are from the tissues, bones, muscles, skin, liver, and heart. All these changes happen before the implantation in the uterus.
Then blastocyst implantation occurs where the zona pellucida breaks and releases the blastocyst. Around the tenth day, the blastocyst moves towards the Fallopian tubes to reach the uterus. It gets implanted in the endometrium of the uterus. The external cells and the uterine inner lining jointly create the future placenta, which transfers nutrients to the baby and removes waste.
Issues that could obstruct Blastocyst Development
Some genetic abnormalities in the sperm or the egg can cause Blastocyst arrest. The arrest means the cells fail to divide, and the embryo’s developmental progress stops. Scientifically, it is known that the endometrium selects the embryo before allowing for the implantation. Any abnormal embryo gets rejected. If there are any abnormal genetic mutations, then implantation fails, causing a miscarriage.
Stage – 3 Embryo Development
After the implantation, the blastocyst evolves into a structure called an embryo. At this stage, most of the internal organs and external structures develop. Below are the organs and systems that develop:-
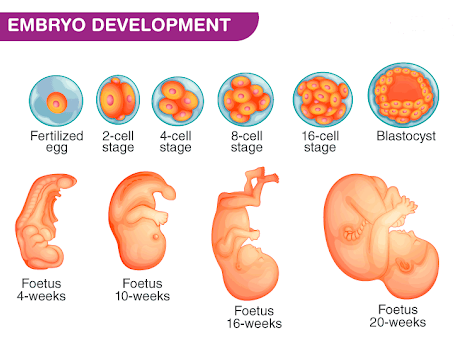
- The mouth, lower jaw, throat
- The blood circulation system evolves
- Heart tube creation starts.
- Ears and eyes start to grow.
- Arms, legs, fingers, toes are shaped.
- The brain, spinal cord, digestive tract and sensory organs start developing.
- The cartilage will be replaced by the initial bones.
In ten to twelve weeks, the embryo moves into a fetus, which is the final stage of embryonic development.
Issues that could obstruct Embryo Development
During this stage, so many internal and external organs start developing. So they can be issues anywhere in the process, especially due to genetic abnormalities and environmental exposures. Genetic abnormalities affect important structures like the heart or brain. Environmental factors like malnutrition, infections, disease, toxic exposures can prove lethal to the developing embryo.
Stage – 4 Fetal Development
At the end of fertilization, the embryo grows into the fetal stage. The fetus is much more robust than the embryo. Hence, the chances of miscarriages at this stage are less. After the second trimester, the fetus can respond to sounds and is 12 inches long and goes up to 14 inches. Around the eighth month, the fetus is called a baby, and it can see and hear, although the respiratory system is not fully matured. Baby weight varies from 2 kg to 4 kg. By the end of pregnancy, i.e., the ninth month, the baby can move, but the space becomes too little for the new human being. This is the time when the baby is ready to be born.
It is important that you stay in touch with your doctor throughout the pregnancy. The mental and emotional state of the mother highly affects the fetus’s growth. It is very important to be happy and take care of yourself, and you can enjoy your pregnancy.
We at ZIVA fertility center are with you throughout the journey. Reach us today at 91-93474 06900 or +91 78424 00104; or email: Info@zivafertility.com